Introduction:
In the world of manufacturing, efficiency and consistency are paramount. SAP PP (Production Planning) offers various methods to cater to the diverse needs of industries, and one such method that has gained prominence in recent years is repetitive manufacturing. This approach involves the production of goods in large quantities with a high degree of repetition. SAP Production Planning offers a comprehensive solution for managing repetitive manufacturing processes.
In this blog, we will delve into what repetitive manufacturing entails, explore its benefits, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to set up and manage Repetitive Manufacturing in SAP PP
SAP PP: Empowering Repetitive Manufacturing
Before we dive deeper into repetitive manufacturing, let’s understand SAP PP and its crucial role in making repetitive manufacturing a streamlined process.
What is SAP Production Planning (PP)?
SAP PP is a robust module that is designed to optimize production planning and execution. It seamlessly integrates various functions such as demand forecasting, production scheduling, material requirements planning, and shop floor control. When it comes to repetitive manufacturing, SAP PP becomes the backbone of efficiency and consistency.
What is Repetitive Manufacturing?
Repetitive manufacturing is a manufacturing process characterized by the repetitive production of the same or similar products, often in large quantities. This method is particularly well-suited for products with high demand and a need for a consistent production process.
Examples of items commonly produced using repetitive manufacturing include consumer goods, electronic devices, and automotive parts.
Benefits of Repetitive Manufacturing:
The adoption of repetitive manufacturing offers numerous advantages: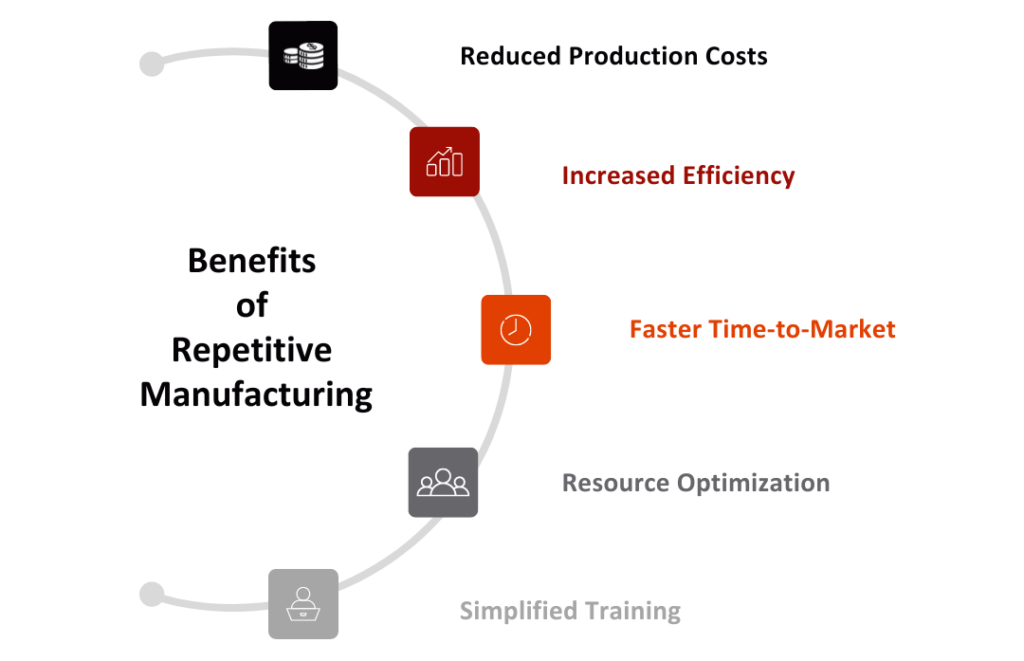
Reduced Production Costs:
Producing goods in large quantities enables companies to leverage economies of scale, resulting in lower production costs per unit.
Increased Efficiency:
Repetitive manufacturing processes are highly standardized, allowing for optimization to improve efficiency. This translates to shorter production times, reduced lead times, and increased throughput.
Faster Time-to-Market:
With standardized processes, repetitive manufacturing allows for quicker product launches, meeting market demands more rapidly and staying ahead of competitors.
Resource Optimization:
Repetitive manufacturing enables the efficient utilization of machinery and labor resources, minimizing downtime and resource idleness, thereby increasing productivity.
Simplified Training:
Standardized procedures make it easier to train new employees, reducing the learning curve and improving workforce flexibility, which is crucial in today’s dynamic manufacturing environments.
Setting up Repetitive Manufacturing in SAP PP:
Implementing repetitive manufacturing in SAP Production Planning (PP) is a systematic process that requires careful configuration and setup. Follow these essential steps to get started:
- Define Production Versions:
Production versions serve as the foundation for your repetitive manufacturing process. They are like the detailed blueprints for your production activities. Each production version should include the following components:
Bill of Materials (BOM):
This is a comprehensive list of all the components and materials required for the assembly of your product. Ensure that your BOM is accurate and up-to-date.
Routing: Routing defines the sequence of operations needed to manufacture the product. It includes details about work centers, operations, and their order. Make sure your routing is well-defined and optimized for efficiency.
- Define Repetitive Manufacturing Profile:
Repetitive manufacturing profiles are critical configuration settings that govern various aspects of your production process. These profiles should include parameters such as:
Production Rates: Specify the rate at which the product should be produced. This parameter ensures that production aligns with demand.
Lot Sizes: Define the lot sizes for production. This helps in optimizing inventory management and production planning.
Order Quantities: Set parameters for order quantities, ensuring that production orders are generated in line with demand forecasts.
- Create Production Orders:
Production orders are the heart of your manufacturing process. They initiate and control production activities. When creating production orders, you need to specify:
Material to Produce: Identify the material or product that you intend to manufacture repetitively.
Quantity to Produce: Define the quantity of the product to be produced in each production order. This should align with your lot sizes and demand forecasts.
Production Version: Select the appropriate production version that you defined earlier. This ensures that the correct BOM and routing are used for each order.
- Monitor Production Progress:
Once production orders are generated and the manufacturing process is underway, it’s crucial to monitor the progress to ensure efficiency and meet production goals. The production order display in SAP PP provides valuable insights into:
Order Status: Check the current status of each production order, whether it’s planned, in progress, or completed.
Production Progress: Track the progress of production orders, including the number of units produced and any delays or issues.
Remaining Capacity: Monitor the capacity of your production resources to ensure they are utilized optimally.
By regularly monitoring production progress, you can make informed decisions and adjustments to maintain a smooth and efficient repetitive manufacturing process.
Master Data for Repetitive Manufacturing:
To effectively implement repetitive manufacturing in SAP PP, specific master data must be maintained:
- Repetitive Manufacturing Profile:
This profile is a vital configuration setting, denoting that a material is intended for repetitive manufacturing. It’s defined in Customizing and linked to the material master record.
- Production Version:
Production versions encompass BOMs and routings and are created within the material master record. They serve as the foundation for production planning.
- Planning ID:
When applicable, planning IDs can be used for planning purposes and should be linked to the material master record.
- Production Line:
For scenarios involving multiple production lines, they can be created and associated with production versions to aid in capacity planning.
- Line Hierarchy (with PP Line Design):
Complex production lines can be represented hierarchically using PP Line Design, especially useful for takt-based scheduling.
- Routing (Rate Routing):
Detailed routing information is essential for capacity planning and scheduling, and rate routing specifies operations and work centers involved.
- Product Cost Collector:
To capture actual production costs, a product cost collector is crucial. It tracks costs related to goods movements and facilitates periodic cost settlement.
Planning Table-Structuring Repetitive Manufacturing:
Repetitive Manufacturing planning and control are organized around time buckets. Starting with existing requirements, production quantities can be planned based on periods, with period views providing effective checks and revisions.
- Sequencing– Coordinating the Manufacturing Ensemble:
Sequencing plays a vital role in determining the order in which planned orders are processed on the production line, particularly in task-based scheduling. It simplifies dispatching, especially for high volumes, and can be visually represented for clarity.
- Pull List– Navigating Material Flow:
The pull list is a control mechanism for managing in-house material flow within production. It monitors stock levels, calculates missing components, and triggers replenishment for a smooth production flow.
- Backflushing– Streamlining Production Completion:
Backflushing simplifies production completion confirmations by automatically referencing the material being produced. It typically involves the backflushing of components and the posting of production costs
- Cost Object Controlling– The Financial Score:
Cost control in Repetitive Manufacturing is often associated with cost objects. These objects can be determined per material or production version, with a product cost collector facilitating cost calculation and tracking over specific periods.
Conclusion:
In Summary, Repetitive Manufacturing, when effectively managed using SAP PP, empowers businesses to produce high-demand goods with consistency and cost-effectiveness. By configuring production versions, maintaining essential master data, and harnessing planning tools like sequencing and the pull list, manufacturers can optimize their repetitive manufacturing processes. Whether producing consumer goods, electronics, or automotive parts, SAP PP in conjunction with Repetitive Manufacturing provides the tools needed to achieve production goals seamlessly.
For SAP PP integration and guidance, reach out to KaarTech’s SAP experts by clicking the link provided.
FAQ’s
What is repetitive manufacturing in SAP Production Planning?
Repetitive manufacturing in SAP Production Planning involves the production of goods in large quantities with a high degree of repetition. It is well-suited for products with high demand and requires standardized processes for efficiency and consistency.
What are the benefits of repetitive manufacturing in SAP PP?
Repetitive manufacturing offers advantages such as reduced production costs through economies of scale, increased efficiency and throughput, faster time-to-market for product launches, resource optimization, and simplified training for new employees.
How do you set up repetitive manufacturing in SAP PP?
To set up repetitive manufacturing in SAP PP, you need to define production versions that include a bill of materials (BOM) and routing. You also need to define a repetitive manufacturing profile with parameters like production rates, lot sizes, and order quantities. Next, you create production orders specifying the material to produce, quantity, and production version. Finally, you monitor production progress to ensure efficiency and meet goals.
What is the importance of master data for repetitive manufacturing in SAP PP?
Specific master data is crucial for effective implementation of repetitive manufacturing in SAP PP. This includes repetitive manufacturing profiles, production versions, planning IDs, production lines, line hierarchy, routing, and product cost collectors.
